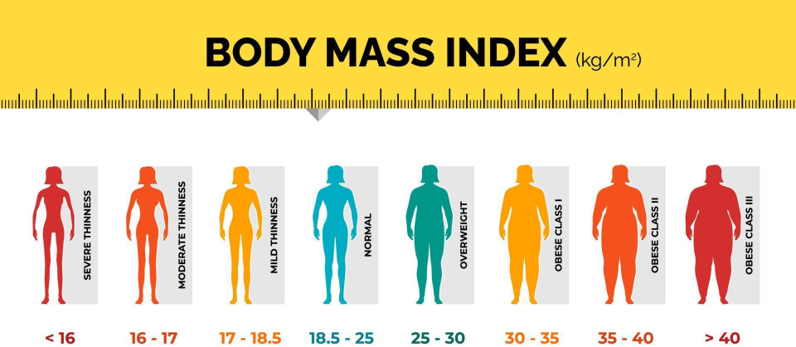
Research how diet and intermittent
fasting are key tools in the management of diabetes

Structured lifestyle programs will consistently outperform medication in terms of prevention, disease reduction and Type 2 Diabetes remission as they form the proven foundation for metabolic repair
Research clearly shows that a poor diet especially when it includes highly processed foods, the absence of basic activity such as short walks & mobility stretches, broken sleep and poor weight control are the most powerful drivers of type 2 diabetes risk
Improving these lifestyle factors can prevent the diabetic condition, slow progression and even reverse Type 2 diabetes into remission if you have the condition
When you eat good quality food, remove ultra processed foods! (UPFs), follow an intermittent fasting schedule that manages when you eat and exercise just a little bit more, these simple changes will have huge benefits for your metabolic repairs
🌱 Click to Expand and Display the Research…..
🩺Title: Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes: ADA Position Statement
💬Extract: A comprehensive lifestyle-prevention overview covering diet, exercise, weight management, and behavioural counselling for maintaining normal glucose regulation. Patients’ perceptions about their own ability, or self-efficacy, to self-manage diabetes are one important psychosocial factor related to improved diabetes self-management and treatment outcomes in diabetes
👉 View Full Research
🩺 Intermittent fasting in the treatment of type 2 diabetes (Dyńka D. et al., 2025)
💬Extract: Summary: The review describes how intermittent fasting (IF) may improve insulin sensitivity, reduce post-meal glucose spikes and lower insulin secretion needs in T2D. fasting (among other lifestyle strategies) could aid T2D remission pathways, particularly when combined with weight loss, diet quality & exercise
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Physical activity and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis.” European Journal of Epidemiology, 2015.
💬Extract: This meta-analysis provides strong evidence for an inverse association between physical activity and risk of type 2 diabetes, which may partly be mediated by reduced adiposity. All subtypes of physical activity appear to be beneficial. Reductions in risk are observed up to 5–7 h of leisure-time, vigorous or low intensity physical activity per week, but further reductions cannot be excluded beyond this range
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and …” Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2022
💬Extract:… some modifiable lifestyle factors including diet, exercise, smoking, sleep and stress are also considered to contribute to IR. For instance, irregular daily eating habits or poor sleep are connected to elevated risk for both obesity and IR
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: 5 year follow up of the randomised Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial (DiRECT) (Lean et al., 2024) •
💬Extract: This is a follow-up of the DiRECT trial: people with T2D (≤ 6 years diagnosis) received a low‐energy diet replacement + weight‐loss support. At 5 years, participants in the intervention group had on average ~6 kg weight loss, and significantly more of them had HbA1c < 48 mmol/mol (≈6.5%) without glucose-lowering medications compared to controls. Key take-away: substantial weight loss (via diet) early after T2D diagnosis can lead to remission (or near-remission) and better health outcomes.
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Mechanisms of insulin resistance in humans and possible links with inflammation
💬Extract: Obesity is a very common cause of insulin resistance. As mentioned above, a potential mechanism for this relationship is ectopic lipid accumulation. However, obesity is also associated with a systemic chronic inflammatory response characterized by altered cytokine production and activation of inflammatory signaling pathways.48 Recent reports have linked this inflammatory response to the development of insulin resistance in 2 different ways. First, activation of inflammatory signaling intermediates may be directly involved in serine phosphorylation of IRS-1 within insulin-sensitive cell types such as hepatocytes and myocytes and thereby in inducing insulin resistance. Second, inflammatory cell infiltration within adipose tissue may be involved in altering adipocyte lipid metabolism (for example, tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α] is reported to promote lipolysis) as well as altering cytokine production by adipose tissue, which may in turn have downstream effects in other metabolically important tissues
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Efficacy of interventions that include diet, aerobic and resistance training in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta analysis (Zhao et al., 2024)
💬Extract: This systematic review and network meta-analysis evaluated physical-activity interventions in working‐age adults with T2D and compared types of exercise (aerobic, resistance, combined) and diet/exercise combinations. Key findings: Combined exercise (especially aerobic + resistance) with diet has stronger effect in improving glycaemic control compared to either alone.
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Harvard School of Public Health — “Simple Steps to Preventing Diabetes”
💬Extract: The good news is that prediabetes and type 2 diabetes are largely preventable. About 9 in 10 cases in the U.S. can be avoided by making lifestyle changes. These same changes can also lower the chances of developing heart disease and some cancers. The key to prevention can be boiled down to five words: Stay lean and stay active
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin
💬Extract: The lifestyle intervention reduced the incidence by 58 percent (95 percent confidence interval, 48 to 66 percent) and metformin by 31 percent (95 percent confidence interval, 17 to 43 percent), as compared with placebo; the lifestyle intervention was significantly more effective than metformin
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Differential role of insulin resistance and β-cell function in the …” Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2019
💬Extract: Demonstrates that increasing insulin resistance is the primary driver of progression from normal glucose tolerance to prediabetes, prior to major β-cell failure
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Skeletal Muscle Insulin Resistance Is the Primary Defect in Type 2 Diabetes
💬Extract: Insulin resistance is a nearly universal finding in patients with established type 2 diabetes. In normal-weight and obese individuals with IGT and in type 2 diabetic subjects with mild fasting hyperglycemia (110–140 mg/dl, 6.1–7.8 mmol/l), both the basal and glucose-stimulated plasma insulin levels are increased
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Continuous Glucose Profiles in Healthy Subjects under Everyday Life Conditions and after Different Meals.” Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 2007
💬Extract: This study provided continuous glucose profiles in nondiabetic subjects and demonstrated that differences in meal composition are reflected in postprandial interstitial glucose concentrations. Regarding the increasing application of continuous glucose monitoring in diabetic patients, these data suggest that detailed information about the ingested meals is important for adequate interpretation of postprandial glucose profile
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and …” Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2022
💬Extract:… No medications exist currently that are specifically approved to treat IR, but IR management91,448,449 is possible through lifestyle changes like dietary, increased exercise, and disease prevention in addition to alternative medications (Fig. 6). Among these treatments, lifestyle changes should be the main focus for IR treatment, with nutritional intervention to decrease calories, avoidance of carbohydrates, and focusing on aliments with low glycemic index (including vegetables, fruits, whole-grain products, nuts, lean meats or beans) to provide higher fiber, vitamins, healthy fats and protein are particularly helpful for people trying to improve insulin sensitivity.450,451,452 A healthy diet and regular physical exercise including approximately 30 minutes of exercise at least five days a week leads to activation of muscle
👉 View Full Research
🩺Title: Insulin and insulin resistance. PubMed Central (PMC), 2005 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 2007
💬Extract: a large body of evidence supports the role of exercise in improving insulin sensitivity and its beneficial outcomes in insulin resistant states. Epidemiological studies such as the US Physicians Health Study have reported substantial decreases in the relative risk of type 2 diabetes with lifelong regular physical activity
👉 View Full Research
🩺 Diet in the management of type 2 diabetes: umbrella review” (2023) by E Szczerba et al
💬Extract: The evidence indicated that diet has a multifaceted role in the management of type 2 diabetes. An energy restricted diet can reduce body weight and improve cardiometabolic health. Beyond energy restriction, dietary approaches such as plant based, Mediterranean, low carbohydrate (<26% total energy), or high protein diets, and a higher intake of omega 3 fatty acids can be beneficial for cardiometabolic health in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
👉 View Full Research








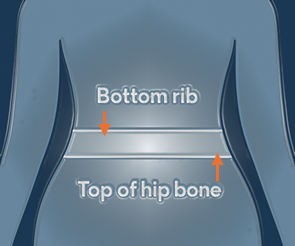
 Use a flexible tape measure (Doh!)
Use a flexible tape measure (Doh!)
 Feel for your bottom rib with your fingers
Feel for your bottom rib with your fingers
 Feel for the top of your hip bone
Feel for the top of your hip bone